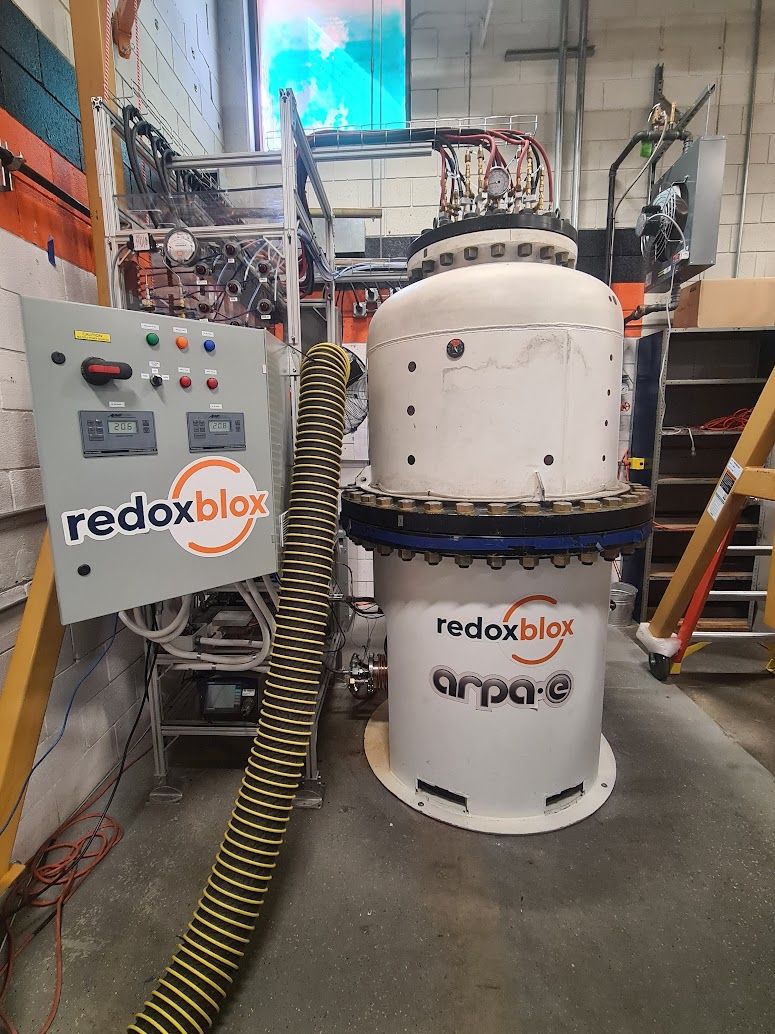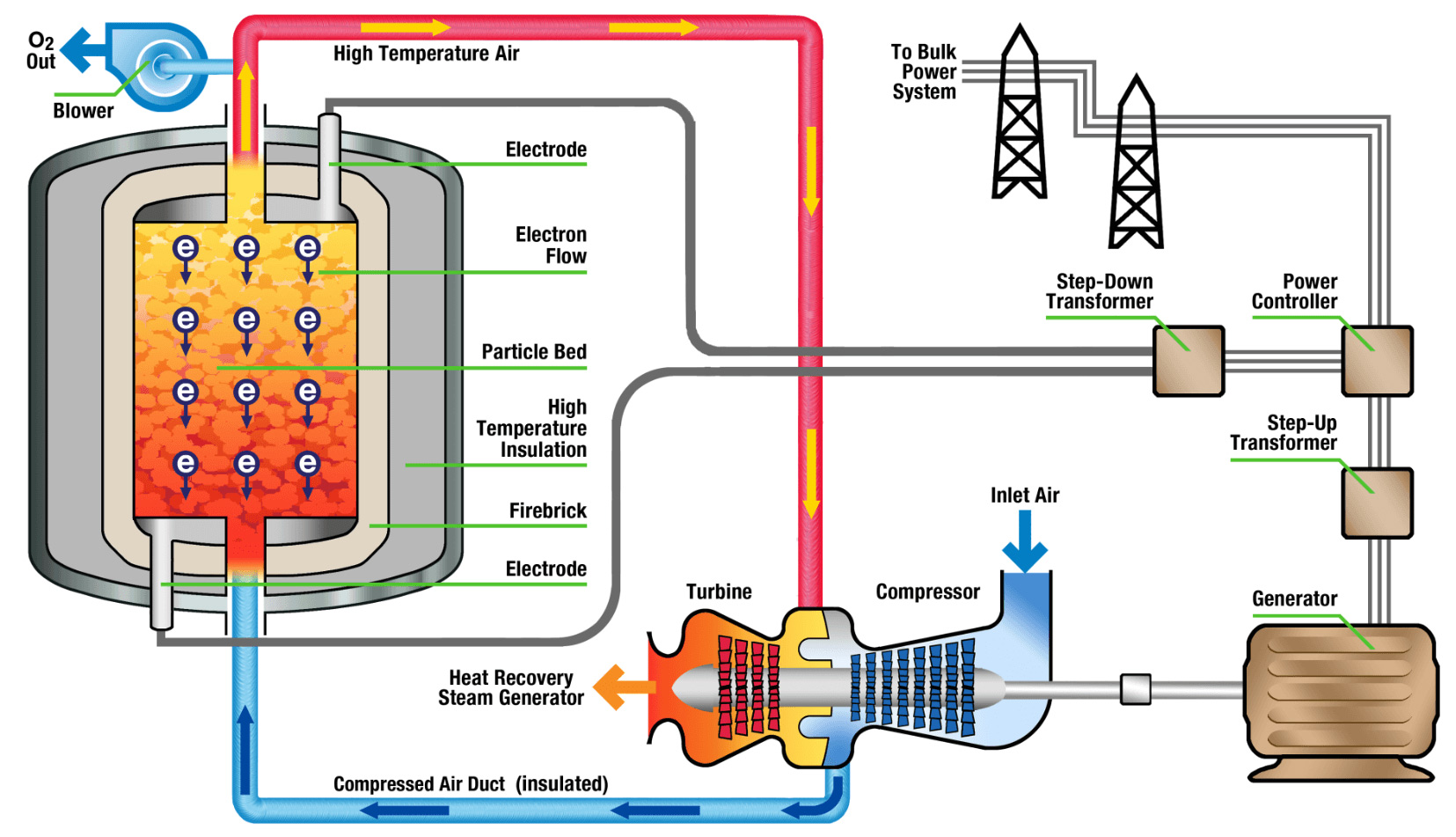
For power generation applications, the RedoxBlox energy storage module consists of a steel pressure vessel containing the proprietary storage material. The module is “charged” using excess renewable electricity from the grid to resistively heat the storage material to temperatures of up to 1500 °C, whereupon the material becomes reduced as it releases pure oxygen gas. Upon “discharge”, pressurized air from the compressor of a gas turbine is forced through the storage material, whereupon oxygen is absorbed and heat released, as the redox material becomes oxidized. The hot (1000-1500 °C) oxygen-depleted air is then delivered to the expander of a gas turbine to produce electrical power.
Industrial Heat Applications
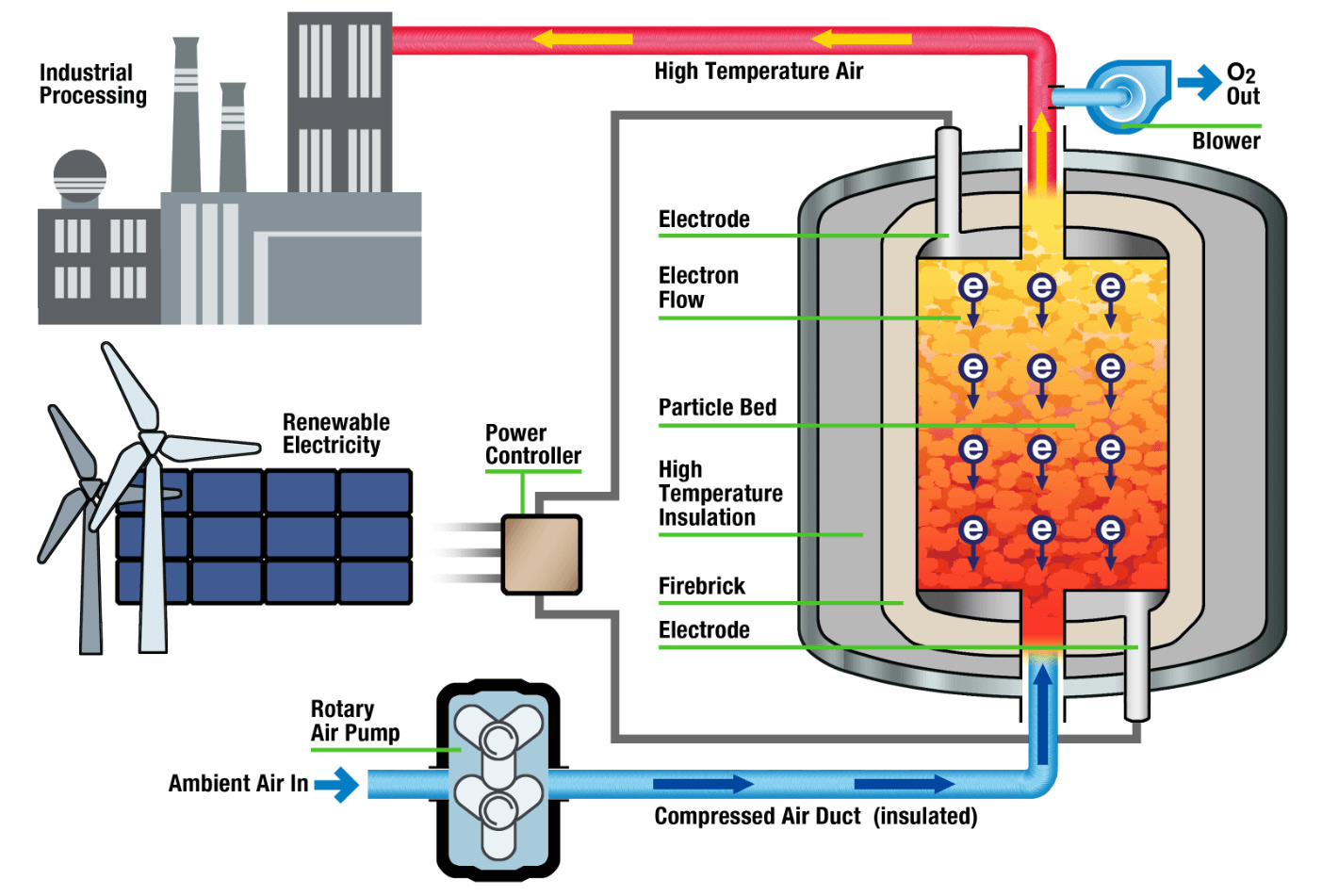
For industrial heat applications, the RedoxBlox energy storage module consists of a low-pressure vessel containing the proprietary storage material. The module is “charged” using excess renewable electricity from the grid to resistively heat the redox material to temperatures of up to 1500 °C, whereupon the material becomes reduced as it releases pure oxygen gas. Upon “discharge”, atmospheric air from an air pump is forced through the storage material, whereupon oxygen is absorbed and heat released, as the redox material becomes oxidized. The hot (1000-1500 °C) oxygen-depleted air is then delivered to the industrial process of interest. Depending on the system architecture, 24/7 delivery of high temperature heat is possible.
What makes our technology unique?
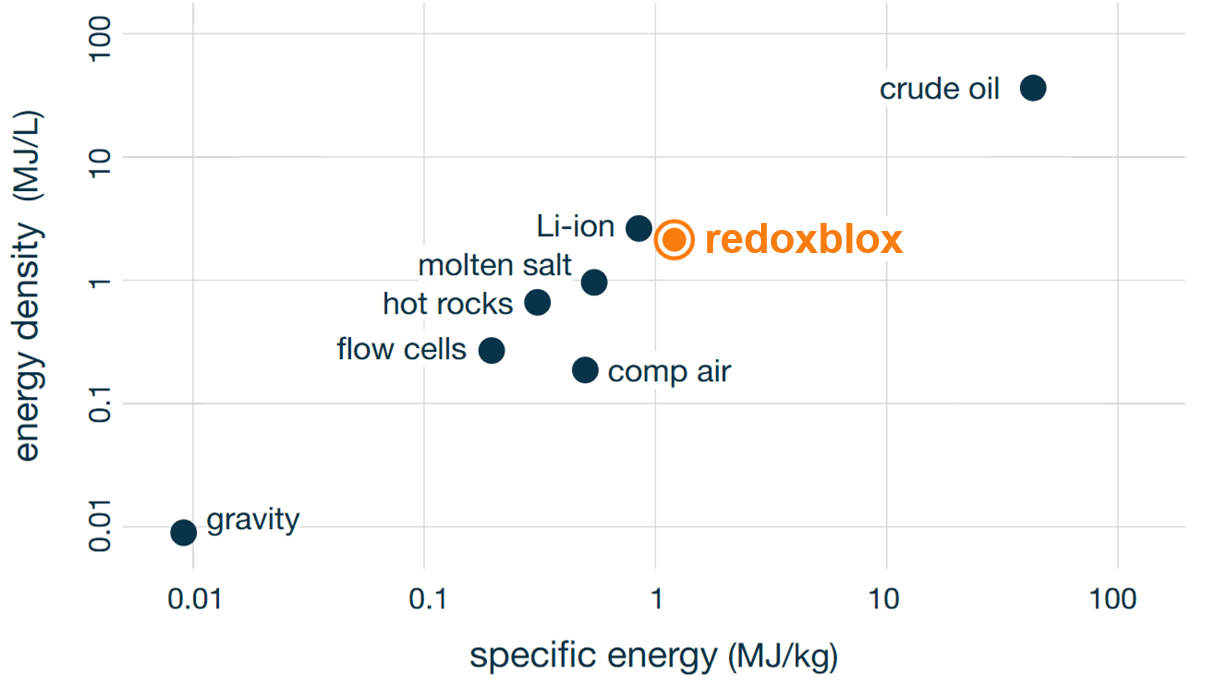
RedoxBlox storage material energy density is on par with lithium-ion technology, while utilizing inexpensive and abundant raw materials. The storage material is also non-toxic, non-flammable, and fully recyclable.
RedoxBlox storage material is unique as it operates at temperatures up to 1500 °C and can be fully charged in less than 4 hours.
Prototypes
Gallery of thermochemical storage reactors manufactured and operated so far.
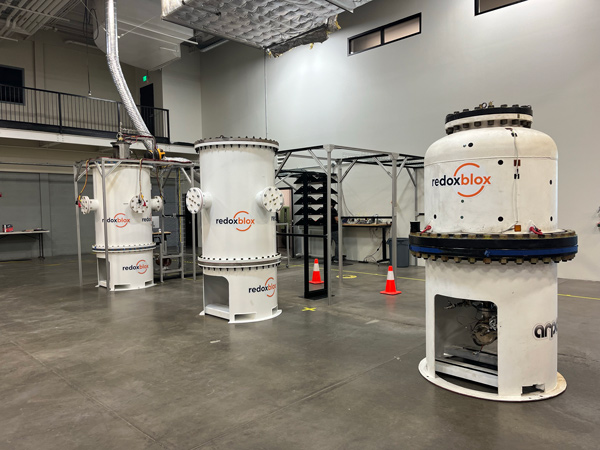

10 kWhth and 100 kWhth units
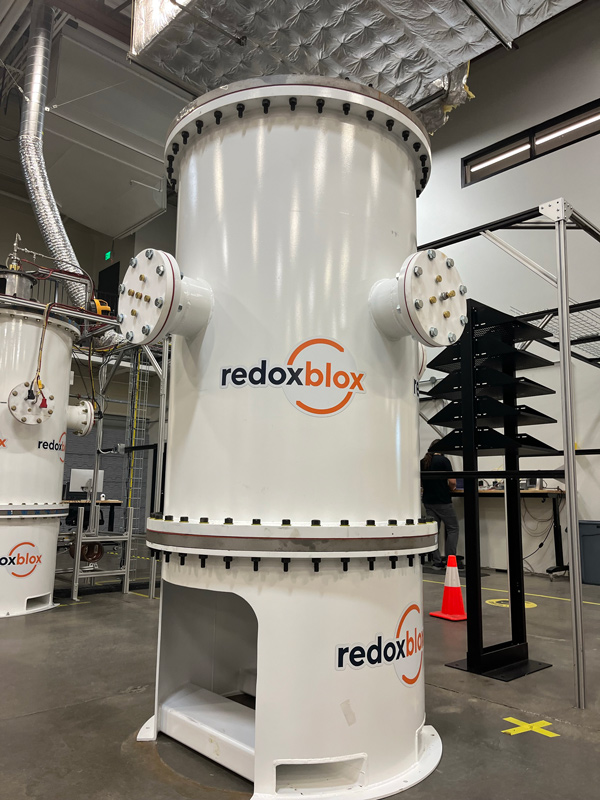

100 kWhth volumetrically heated